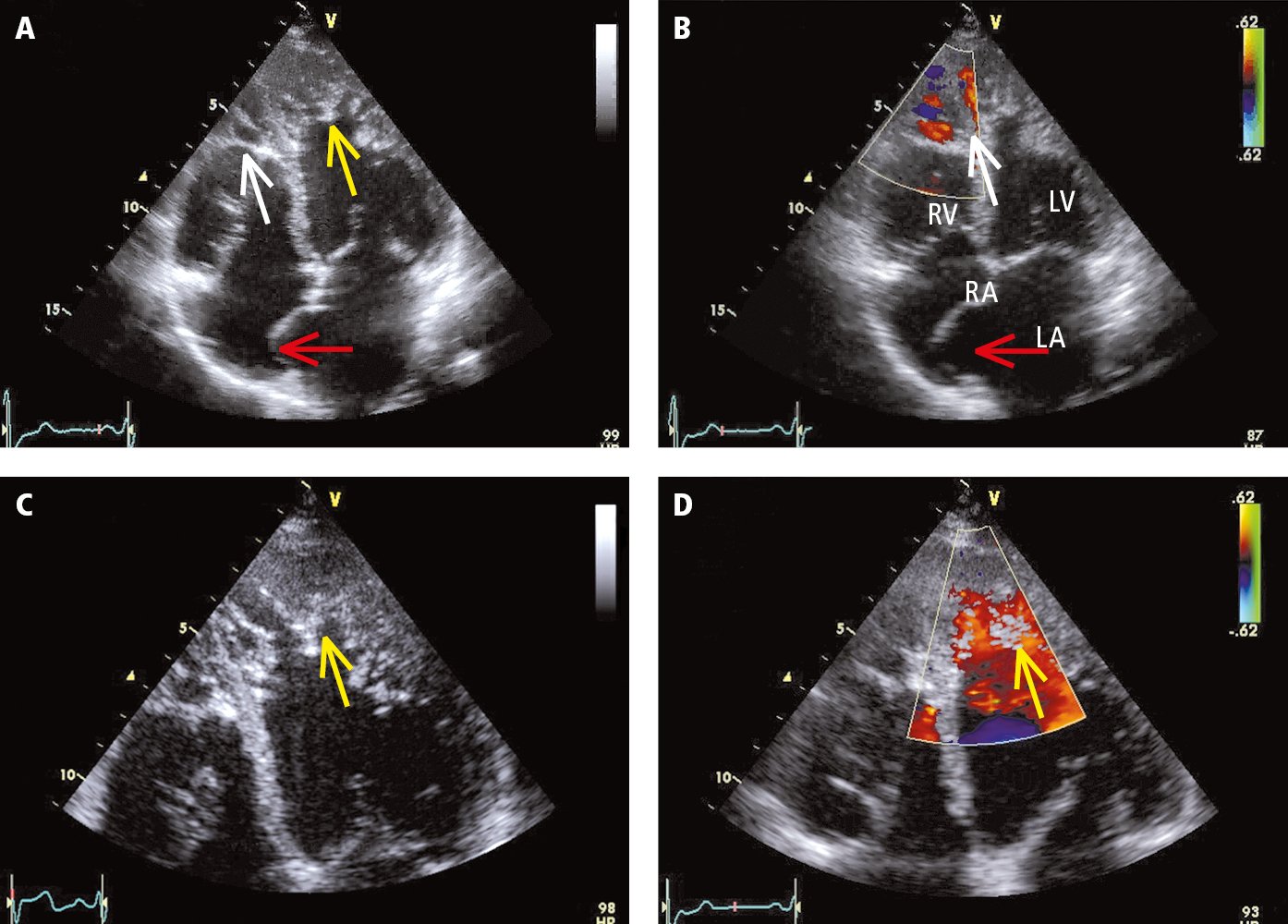
Figure 031_2319.
Transthoracic echocardiography (TTE) of a patient with left ventricular noncompaction (apical 4-chamber view, standard probe placement): A, 2D imaging; B, color Doppler examination; C, enlarged panel A; D, color Doppler examination. Yellow arrows mark the spongiform structure of the myocardium in the mid and apical segments of the left ventricle (LV). The layer of the abnormal cardiac muscle is more than twice as thick as the healthy compact layer. A healthy apex of the right ventricle (RV) usually has numerous myocardial trabeculae. For this reason, despite the significantly increased trabeculation (white arrow), it is not clear if this finding can be considered abnormal. Color Doppler revealed blood flow penetrating deep into both ventricular apexes, which indicates that tissue in this area is not solid (a solid tissue structure would be typical for apical hypertrophic cardiomyopathy or ventricular cavities filled with thrombi or other masses). The interatrial septum is markedly protruding to the right (red arrow), which meets the diagnostic criteria for atrial septal aneurysm. LA, left atrium; RA, right atrium. Figure courtesy of Dr Andrzej Gackowski.