Kalil AC, Metersky ML, Klompas M, et al. Management of Adults With Hospital-Acquired and Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia: 2016 Clinical Practice Guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America and the American Thoracic Society. Clin Infect Dis. 2016 Sep 1;63(5):e61-e111. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciw353. Epub 2016 Jul 14. PMID: 27418577; PMCID: PMC4981759.
National Clinical Guideline Centre (UK). Pneumonia: Diagnosis and Management of Community- and Hospital-Acquired Pneumonia in Adults. London: National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (UK); 2014 Dec. PMID: 25520986.
Woodhead M, Blasi F, Ewig S, et al; Joint Taskforce of the European Respiratory Society and European Society for Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases. Guidelines for the management of adult lower respiratory tract infections--summary. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2011 Nov;17 Suppl 6:1-24. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2011.03602.x. PMID: 21951384.
Limper AH, Knox KS, Sarosi GA, et al; American Thoracic Society Fungal Working Group. An official American Thoracic Society statement: Treatment of fungal infections in adult pulmonary and critical care patients. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2011 Jan 1;183(1):96-128. doi: 10.1164/rccm.2008-740ST. PMID: 21193785.
Lim WS, Baudouin SV, George RC, et al; Pneumonia Guidelines Committee of the BTS Standards of Care Committee. BTS guidelines for the management of community acquired pneumonia in adults: update 2009. Thorax. 2009 Oct;64 Suppl 3:iii1-55. doi: 10.1136/thx.2009.121434. PMID: 19783532.
Torres A, Ewig S, Lode H, Carlet J; European HAP working group. Defining, treating and preventing hospital acquired pneumonia: European perspective. Intensive Care Med. 2009 Jan;35(1):9-29. doi: 10.1007/s00134-008-1336-9. PMID: 18989656.
Mandell LA, Wunderink RG, Anzueto A, et al; Infectious Diseases Society of America; American Thoracic Society. Infectious Diseases Society of America/American Thoracic Society consensus guidelines on the management of community-acquired pneumonia in adults. Clin Infect Dis. 2007 Mar 1;44 Suppl 2:S27-72. PMID: 17278083.
American Thoracic Society; Infectious Diseases Society of America. Guidelines for the management of adults with hospital-acquired, ventilator-associated, and healthcare-associated pneumonia. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2005 Feb 15;171(4):388-416. PMID: 15699079.
Definition, Etiology, PathogenesisTop
Hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP) is a pneumonia that develops after 48 hours of hospitalization in a patient who has not been intubated on admission. Ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP) is a pneumonia that develops after >48 hours of starting mechanical ventilation.
Etiologic agents:
1) Within the first 4 days of admission etiologic agents may be the same as in the case of community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) and may also include gram-negative bacilli (Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Enterobacter spp, Proteus spp, and Serratia spp).
2) From day 5 onwards etiologic agents are more likely to include multidrug-resistant strains, typically aerobic gram-negative bacilli: Pseudomonas aeruginosa, E coli, K pneumoniae, Acinetobacter spp, and more rarely Legionella pneumophila. The predominant gram-positive bacterium is Staphylococcus aureus, whose hospital strains may be resistant to methicillin. The bacterial flora and its resistance to antibiotics differ among hospitals, therefore each hospital should develop its own profile of microbes causing hospital infections along with their drug sensitivity (separate for the intensive care unit [ICU]).
3) Pneumonia caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) may need to be taken into account in the diagnostic process and determination of empiric treatment: see Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19).
4) Risk factors for multidrug-resistant VAP: IV antibiotic therapy during the previous 90 days, septic shock, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), duration of current hospitalization ≥5 days, renal replacement therapy for acute indications prior to the appearance of VAP symptoms.
5) Risk factors for infection with multidrug-resistant P aeruginosa strains and other intestinal bacteria: Admission to an ICU where >10% of VAP-causing gram-negative strains are resistant to antibiotic monotherapy or the sensitivity of the local flora to antibiotics is unknown, or earlier colonization with P aeruginosa or other gram-negative intestinal bacteria.
6) Risk factors for methicillin-resistant S aureus (MRSA) infection: Stay in a unit where >10% to 20% of VAP-related S aureus strains are resistant to methicillin or the frequency of isolation of MRSA strains is unknown, or earlier isolation of MRSA in the patient.
The sources of pathogens are medical devices and the environment (air, water, equipment, clothing), but the pathogens can be also transmitted between the patient and the medical personnel or other patients.
Clinical Features and Natural HistoryTop
Clinical features are the same as in CAP (see Community-Acquired Pneumonia) and frequently include change in sputum volume and/or character (color, purulency). Mortality rates in patients with HAP developing after surgery are ~20%. In patients treated in the ICU, the mortality rates are 30% to 40%.
DiagnosisTop
Diagnostic tests are the same as in CAP (see Community-Acquired Pneumonia). Prior to any modification of antimicrobial treatment in patients with suspected HAP, collect samples from the lower respiratory tract material (obtained by endotracheal aspiration, bronchoalveolar lavage, or protected specimen brushing). Blood cultures should be performed in all patients with suspected VAP; a positive result may be indicative of pneumonia or an extrapulmonary infection. Levels of inflammatory markers (C-reactive protein [CRP] or procalcitonin) have a limited role in the diagnosis of VAP.
Complications of an underlying condition, such as pulmonary embolism and pulmonary infarct (resulting from immobilization and deep vein thrombosis), sepsis (may be complicated by acute respiratory distress syndrome), or alveolar bleeding in the course of a systemic disease.
TreatmentTop
Management of patients with HAP, VAP, and HCAP is similar.
General measures are as in CAP (see Community-Acquired Pneumonia).
Selection of antimicrobial agents: see Table 17.17-1. Management algorithm: Figure 17.17-4.
1. Empiric treatment is modified on day 2 or 3 of therapy based on the clinical response and culture results. Start from IV antibiotics (in the case of fluoroquinolones and linezolid, you may switch to oral administration immediately after achieving clinical improvement):
1) Patients hospitalized for <5 days without risk factors of drug resistance: Treatment with one antibiotic: ceftriaxone or a respiratory fluoroquinolone (levofloxacin or moxifloxacin). In the case of MRSA colonization or high-risk patients, add vancomycin. In the case of colonization with bacteria producing extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL), use ertapenem or meropenem (instead of ceftriaxone or a respiratory quinolone).
2) Patients hospitalized for ≥5 days at risk of drug resistance (one of the following):
a) Meropenem.
b) A beta-lactam with a beta-lactamase inhibitor (piperacillin with tazobactam, ticarcillin with clavulanic acid).
Note that if the patient is at increased risk of multidrug-resistant P aeruginosa infection, adding an extra antibiotic with antipseudomonal activity (eg, fluoroquinolone) is recommended.
Note that if the patient is at increased risk of MRSA infection, adding vancomycin or linezolid is reasonable.
2. After identifying the etiologic agent, switch to targeted therapy when indicated. Therapy should be as short as possible (up to 7 days, except for P aeruginosa infections, S aureus infections, and immunocompromised patients). In patients with Acinetobacter spp infection, use carbapenems, ampicillin plus sulbactam, or colistin. In patients suspected to have infections caused by Enterobacteriaceae producing ESBL, carbapenems are recommended.
Follow-UpTop
Assess the clinical response to antimicrobial treatment after 48 to 72 hours. Resolution of fever, decrease in white blood cell counts, increase in blood oxygen saturation, and improved general condition confirm the effectiveness of treatment. If no improvement is observed, repeat microbiologic tests (if invasive testing is considered, repeat imaging to determine the optimal target) and consider a different etiology (mycobacterial or fungal) or diagnoses other than pneumonia.
FiguresTop
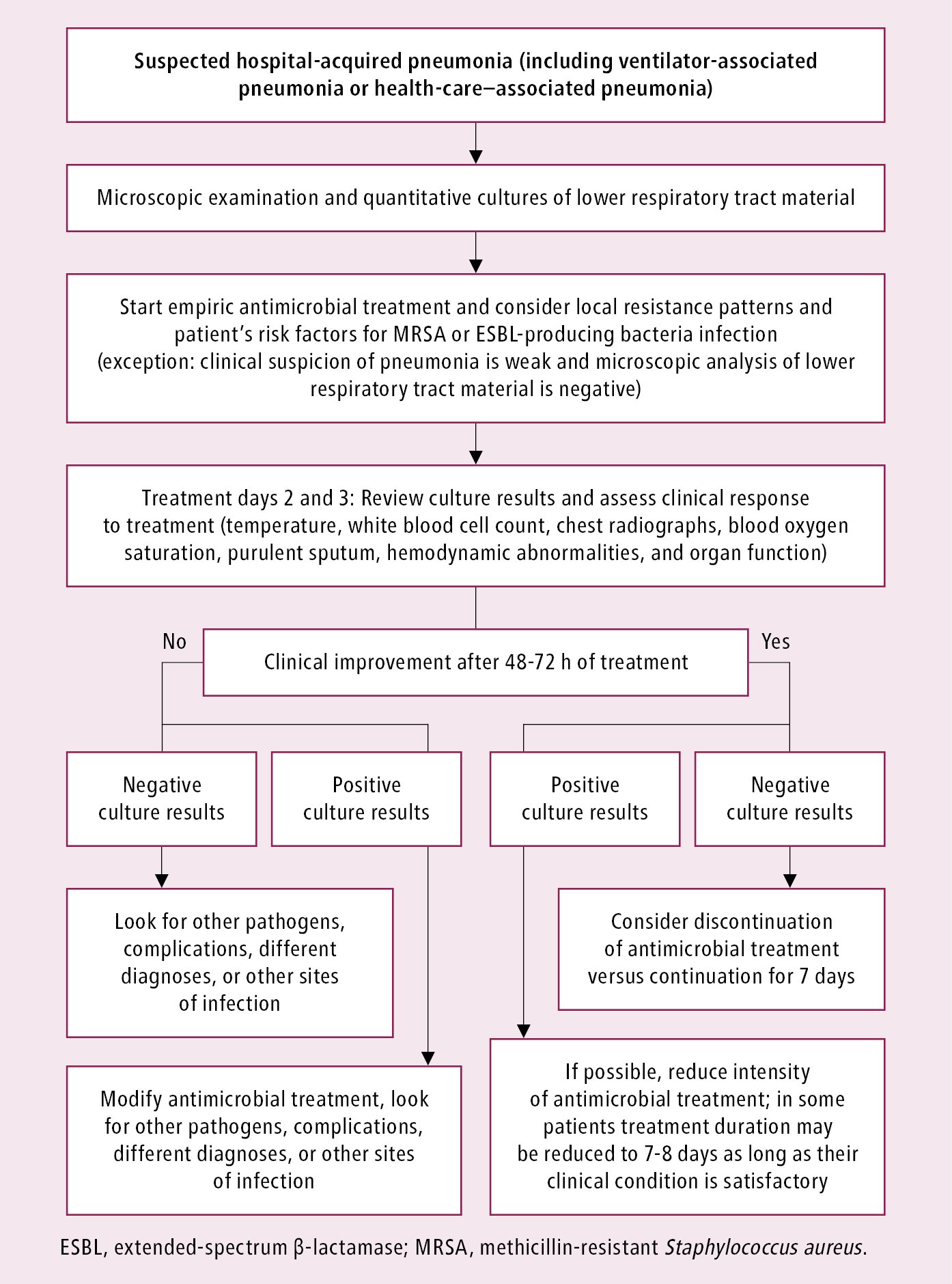
Figure 17.17-4. Management algorithm in patients with suspected hospital-acquired pneumonia.